
Introduction: Composing with AI
Nupoor Ranade and Douglas Eyman
Histories: C&W Approaches to Disruptive Technologies

Nupoor Ranade and Douglas Eyman

Anthony Atkins and Colleen A. Reilly
This chapter examines past responses to the challenges posed to conceptions of writing and authorship; the access and accessibility implications of information and communication technologies; and the degree to which technologies reveal and mask their mediation of content, and how we can support our responses to AI based on past encounters with new technologies.

Antonio Hamilton and Finola McMahon
Examining current automated writing evaluation (AWE) applications, the authors found three central themes. 1.) The user's technical illiteracy being used against them to prevent a full understanding of the programs prior to purchase, 2.) The programs' websites obscuring details about how the algorithms function, and 3.) Black-boxing as an appeal to current-traditional rhetoric and the use of static abstractions in writing feedback.
Policy: Programs and Publications

Dan Frank and Jennifer Johnson
Frank and Johnson present a dialectical conversation reflecting on the incorporation of generative AI tools in the writing classroom. They trace the development of the UCSB Writing Program's Policy on ChatGPT and AI Writing, which aims to provide ethical guidance and support for faculty and students in using these technologies.

James P. Purdy
Purdy examines updates to submission policies of academic journals and publishers that were published within six months of ChatGPT’s initial public release. In arguing that generative AI cannot be listed as an author, these policies define what authors, and by extension writing, are and should be.
Reports from the Field: Classes & Students Using AI

Lee-Ann Kastman Breuch, Kathleen Bolander, Alison Obright, Asmita Ghimire, Stuart Deets, and Jessica Remcheck
This chapter shares results of a contextual usability inquiry study of student impressions of ChatGPT. Students completed five tasks using ChatGPT and rated the outputs in terms of expectations, satisfaction, credibility, and relevance. Students consistently rated ChatGPT texts as high in relevance and expectations, but lower in terms of satisfaction and credibility.

Mark C. Marino
AI tools present yet another divisive wedge between the digitally literate haves and the less literate have-nots, and as students' understanding of these systems increases, the potential for productive, creative, and critical use of these tools likewise increases. This chapter details the experimental assignments, in class work, and theoretical bases that led to those findings.

Jeanne Law, James Blakely, John C. Havard, and Laura Palmer
This chapter presents findings from a study of first-year students' perceptions of gen-AI, measuring student attitudes toward gen-AI in both academic and personal writing contexts. Technical communications students were more accepting of gen-AI than first-year writing students across contexts, reflecting their comfort integrating new technologies in their work.
Multimodal Composing: AI Text-to-Image Applications

Jamie Littlefield
AI’s entrenchment in the past generates an algorithmic resistance to change, creating synthetic output that uncritically re-creates values and social structures. In the writing classroom, speculative design practices can provide students with concrete approaches to analyzing and composing AI-generated images that demonstrate awareness of the ways AI reproduces the past.
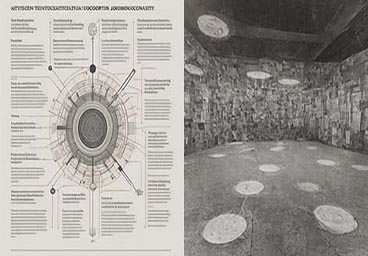
Sierra S. Parker
This chapter analyzes biases (re)produced by text-to-image generative AI compositions, presenting a critical approach that engages technology bias and visual pedagogies of artificial intelligence for the rhetoric and writing classroom. Demonstrating how AI images direct the viewer, the author offers strategies for using this technology meaningfully in the classroom as an object of critical analysis.
Teaching AI Literacies

Christopher Eisenhart
Eisenhart examines the capacities of generative AI applications to engage in the editing and revision work of style by putting ChatGPT through the exercises presented in Joseph Williams's Style: Lessons in Clarity and Grace, noting where it performed as well as a human student, but also where its struggles were similar to those of many first-year writing students.

Patrick Love
This chapter presents the DIKW pyramid, a graphic that Information Theory uses to rationalize the theoretical relationships between data, information, knowledge, and wisdom as part of teaching machines to participate in knowledge-work. The chapter demonstrates connections between DIKW, circulation theory, and active learning pedagogy that can be applied in composition classes.

Desiree Dighton
By integrating heuristic development and analysis into classroom practices, this study aims to enhance students' understanding of AI technologies, fostering critical engagement and agency. The findings highlight the importance of situating AI tools within broader socio-cultural contexts, advocating for a more inclusive and reflective approach to integrating AI in educational settings.